The Boeing Starliner, a pioneering spacecraft designed for commercial crew missions, has garnered significant attention within the aerospace industry. This meticulously crafted overview delves into the Starliner’s capabilities, design, missions, challenges, and future prospects, providing a comprehensive understanding of this groundbreaking spacecraft.
As a cornerstone of NASA’s commercial crew program, the Starliner is poised to revolutionize space exploration. Its advanced design and innovative features make it a formidable contender in the burgeoning commercial space sector.
Boeing Starliner
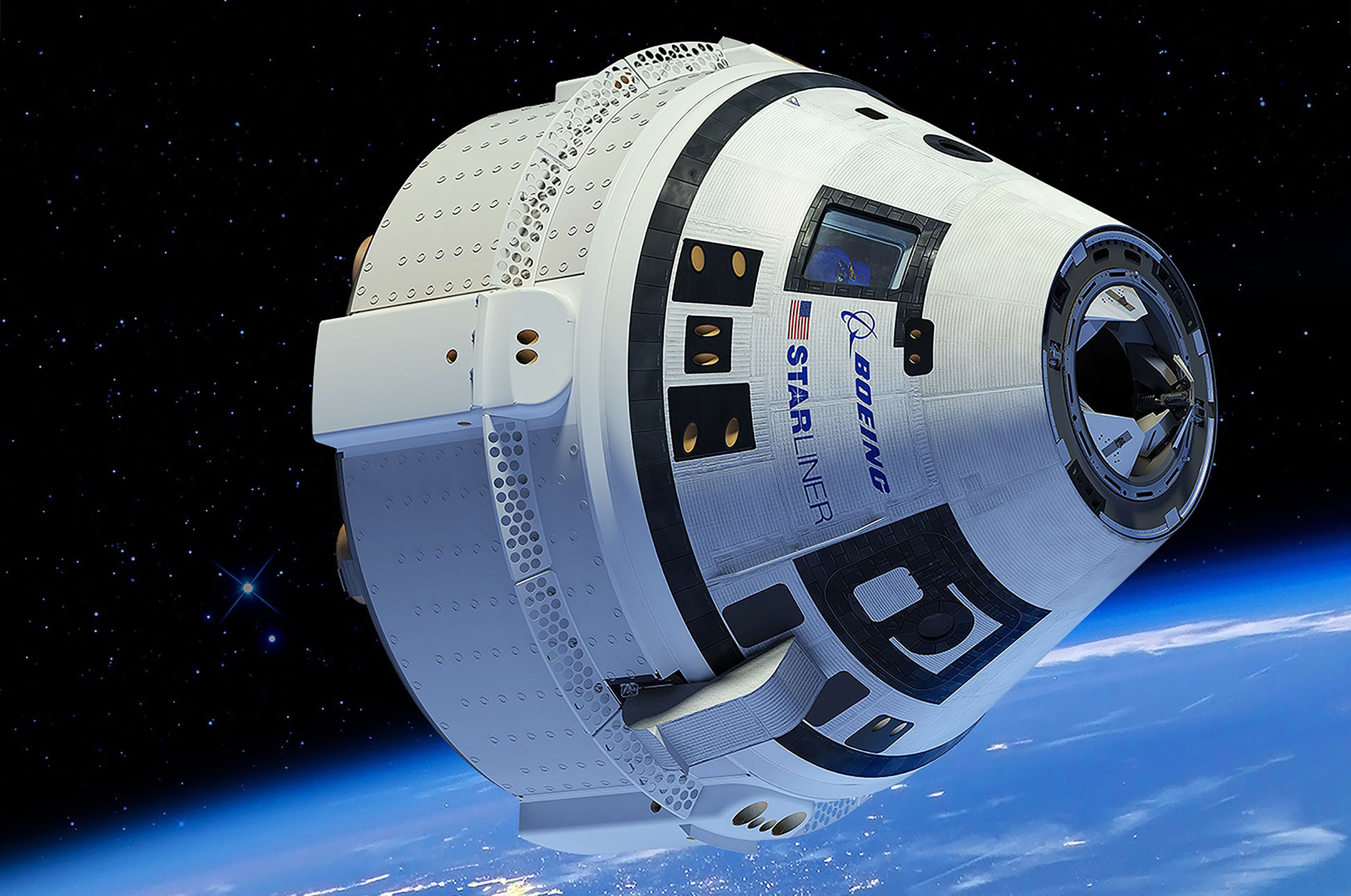
The Boeing Starliner is a reusable spacecraft designed to transport crew and cargo to and from low Earth orbit. It is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which aims to develop spacecraft capable of carrying astronauts to the International Space Station.
Development and Testing
The Starliner’s development began in 2010. It has undergone extensive testing, including a successful uncrewed flight to the International Space Station in 2019. The spacecraft is expected to carry its first crew in 2023.
Starliner’s Design and Features
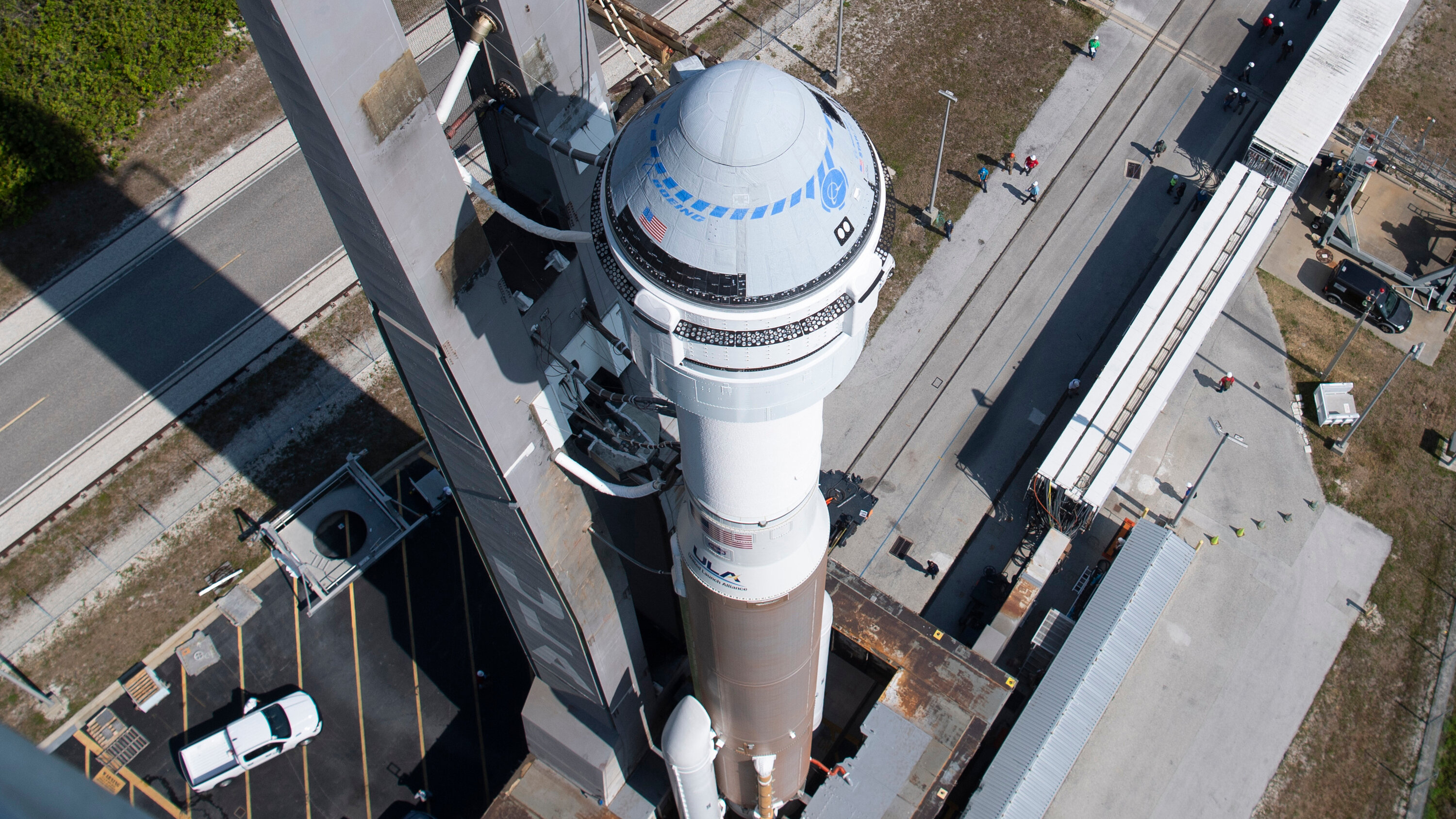

The Boeing Starliner is a reusable spacecraft designed to transport astronauts and cargo to and from low Earth orbit (LEO). It is intended to be a cost-effective and reliable alternative to existing spacecraft such as the SpaceX Crew Dragon and Orion.The Starliner has a unique design that incorporates several key features and systems.
These include a sleek, aerodynamic shape that minimizes drag during atmospheric re-entry, a modular design that allows for easy maintenance and upgrades, and a state-of-the-art avionics suite that provides advanced navigation and communication capabilities.
Propulsion
The Starliner is powered by a single RS-25 rocket engine, which is the same type of engine used on the Space Shuttle. The RS-25 is a powerful and efficient engine that provides the Starliner with the necessary thrust to reach orbit.
In addition to the RS-25, the Starliner also has a set of auxiliary thrusters that are used for maneuvering in space.
Navigation
The Starliner uses a combination of GPS, inertial navigation, and star tracking to navigate in space. The GPS system provides precise positioning data, while the inertial navigation system tracks the Starliner’s movement and orientation. The star tracking system uses the positions of stars to determine the Starliner’s location and attitude.
Communication
The Starliner has a sophisticated communication system that allows it to communicate with ground control and other spacecraft. The communication system includes a variety of antennas that are used for different purposes, such as transmitting data, voice, and video.
Comparison with Other Spacecraft, Boeing starliner
The following table compares the Starliner’s design to that of two other similar spacecraft, the SpaceX Crew Dragon and the Orion.| Feature | Starliner | Crew Dragon | Orion ||—|—|—|—|| Length | 5.5 m | 5.3 m | 5.6 m || Diameter | 4.6 m | 4.2 m | 5.0 m || Mass | 13,000 kg | 12,000 kg | 26,000 kg || Crew Capacity | 7 | 7 | 6 || Cargo Capacity | 2,500 kg | 2,200 kg | 3,000 kg || Propulsion | RS-25 rocket engine | SuperDraco engines | RS-25 rocket engines || Navigation | GPS, inertial navigation, star tracking | GPS, inertial navigation, star tracking | GPS, inertial navigation, star tracking || Communication | Variety of antennas | Variety of antennas | Variety of antennas |
Starliner’s Missions and Objectives
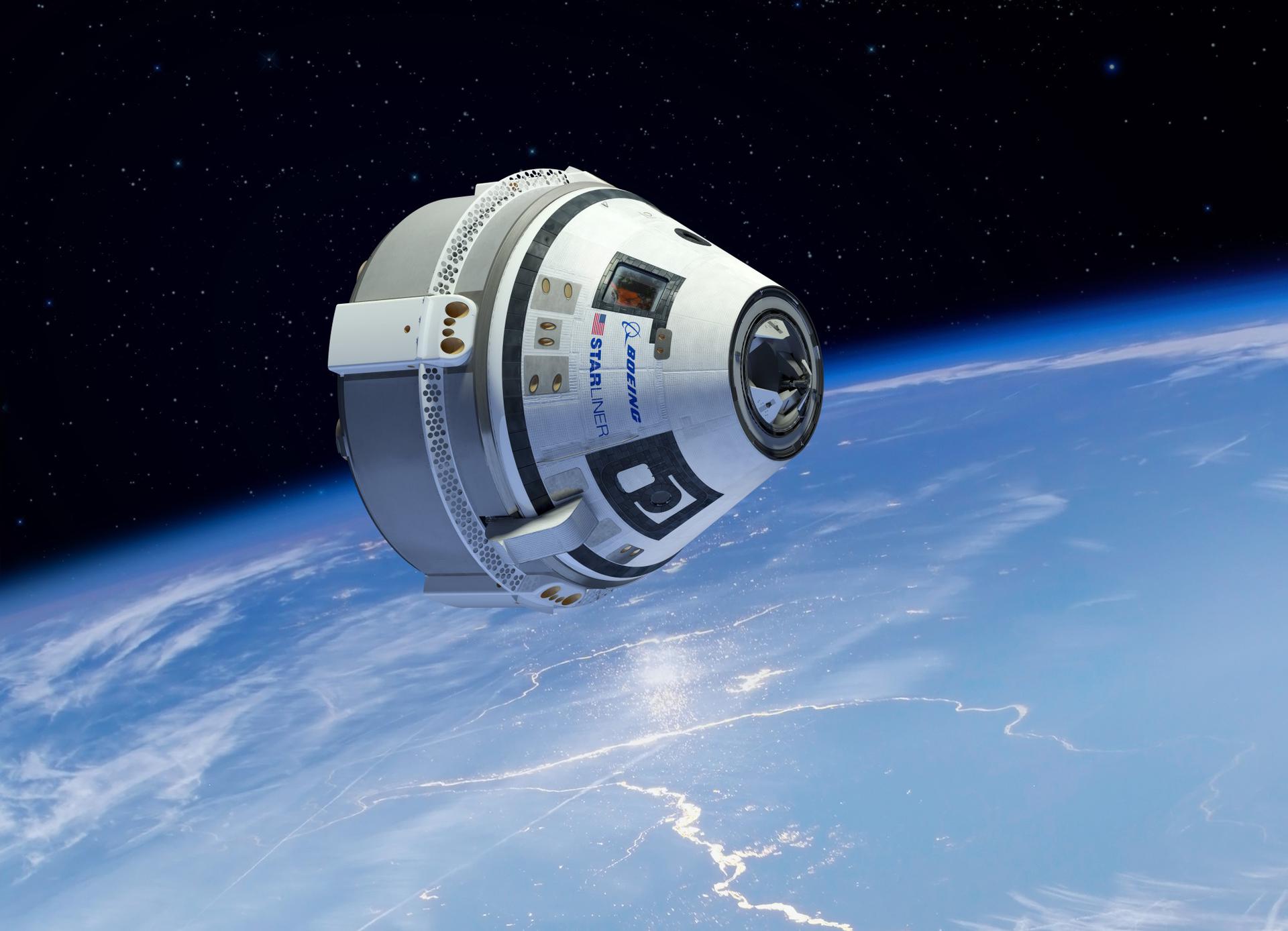

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is designed to fulfill a range of missions, primarily focusing on transporting astronauts and cargo to and from low Earth orbit (LEO). It plays a crucial role in NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which aims to foster the development of private spacecraft capable of ferrying humans to the International Space Station (ISS).
Beyond its role in the Commercial Crew Program, the Starliner is also envisioned as a platform for future space exploration endeavors. Its versatility allows it to support missions to lunar orbit and even Mars, expanding human presence beyond LEO.
Planned and Completed Starliner Missions
- Boeing Orbital Flight Test (OFT): The OFT mission, launched in December 2019, was an uncrewed flight test to demonstrate the Starliner’s capabilities in orbit. The spacecraft successfully docked with the ISS and returned to Earth, paving the way for future crewed missions.
- Crew Flight Test (CFT): The CFT mission, scheduled for launch in 2023, will be the first crewed flight of the Starliner. It will carry a crew of four astronauts to the ISS for an extended stay, further validating the spacecraft’s systems and capabilities.
- Operational Missions: Following the successful completion of the CFT mission, the Starliner is expected to commence regular operational missions to the ISS, transporting astronauts and cargo to and from the orbiting laboratory.
Starliner’s Challenges and Controversies
The Boeing Starliner program has faced several challenges and controversies during its development and testing phases. These issues have impacted the program’s timeline and raised concerns about the spacecraft’s reliability.
Some of the major challenges and controversies associated with the Starliner program include:
Technical Issues
- Software glitches during the first uncrewed test flight (OFT-1) in 2019, which prevented the spacecraft from docking with the International Space Station (ISS).
- Problems with the spacecraft’s propulsion system, leading to delays in the OFT-2 mission.
- Manufacturing defects discovered in the spacecraft’s thrusters, requiring extensive rework.
Delays
- Multiple delays in the program’s schedule, pushing back the target date for crewed missions.
- The OFT-2 mission was delayed by over two years due to technical issues and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cost Overruns
- The Starliner program has faced significant cost overruns, with estimates now exceeding the original budget.
- The delays and technical issues have contributed to the increased costs.
NASA’s Scrutiny
- NASA has closely scrutinized the Starliner program due to the technical issues and delays.
- The agency has conducted independent reviews and implemented additional oversight measures to ensure the spacecraft’s safety and reliability.
Starliner’s Future Prospects

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft has a promising future, with potential applications and uses in various space exploration missions. As a reusable spacecraft, Starliner is designed for multiple missions, offering cost-effective and sustainable access to space.Starliner plays a crucial role in Boeing’s overall space exploration strategy, complementing the company’s other spacecraft, such as the CST-100 Starliner and the Dream Chaser.
Boeing aims to establish a comprehensive space transportation system that caters to different mission requirements and supports long-term human presence in space.
Future Starliner Missions and Developments
Starliner has several upcoming missions planned, including:
- Crewed Flight Test (CFT): A mission to demonstrate Starliner’s ability to safely transport astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS).
- Starliner-1: The first operational mission to the ISS, carrying cargo and supplies.
- Starliner-2: A mission to deliver astronauts to the ISS for a six-month stay.
Beyond these missions, Boeing is exploring future applications for Starliner, including:
- Lunar Gateway Support: Starliner could provide crew transportation and cargo delivery services to the Lunar Gateway, a planned space station in lunar orbit.
- Mars Exploration: Starliner could be used as a crew transport vehicle for future missions to Mars, supporting long-duration human exploration of the Red Planet.
- Commercial Space Tourism: Starliner could offer opportunities for private individuals and space enthusiasts to experience space travel.
The expected timeline for future Starliner missions and developments is subject to various factors, including funding, technological advancements, and international cooperation. However, Boeing is committed to the ongoing development and utilization of Starliner as a versatile and reliable spacecraft for space exploration and commercial space ventures.
Closing Notes
The Boeing Starliner stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the unwavering pursuit of space exploration. Its future missions hold immense promise for scientific discovery, commercial ventures, and the advancement of our understanding of the cosmos.